Studies of Family Concordance Patterns for Schizophrenia Have Found
Learn about the nursing care management of patients with schizophrenia.
What is Schizophrenia?
Despite it existence one of the most common psychiatric disorders, schizophrenia is unremarkably misunderstood. Here is how it is described and defined:
- Schizophrenia refers to a grouping of astringent, disabling psychiatric disorders marked past withdrawal from reality, illogical thinking, possible delusions and hallucinations, and emotional, behavioral, or intellectual disturbance.
- These disturbances terminal for at least for six (6) months. The level of functioning in work, interpersonal relationship, and cocky-care are markedly below the level since the onset of symptoms.
- Have difficulty distinguishing reality from fantasy. Their speech and beliefs may frighten or mystify those around them.
Incidences
Schizophrenia occurs in all societies without regard to class, color, and civilization.
- It affects ane.i% of the population in a higher place age 18, which is estimated to exist 51 million people worldwide.
- In the United States alone, 2 million Americans each year are affected, with seven.2 in 1000 persons developing it during their lifetime.
- Affects both men (belatedly teens or early on 20s) and women (mid-20s to early 30s) every bit
- Prevalence is higher than diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer'southward disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Causes
Like many diseases, schizophrenia is linked to various factors.
- Precise crusade isunknown.
- There is currently no way to predict who volition develop the illness.
- Genetic factors. It is believed that multiple genes (strongest evidence points to chromosomes 13 and 6) are involved in predisposition to schizophrenia. Other factors like prenatal infections, perinatal complications, and environmental stressors are also existence studied. The manner of transmission of genetic predisposition is not clearly understood.
- Biochemical factors. Involves dopamine (focus of most studies), serotonin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Excessive dopamine activity is linked to hallucinations, agitation, and delusion. High norepinephrine is linked to positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
- Other factors include structural brain abnormalities (e.thou. enlarged ventricles), developmental (eastward.g. faulty neuronal connections), and other possible causes (e.one thousand. maternal influenza during second trimester of pregnancy, epilepsy of the temporal lobe, head injury, etc.)
Signs and Symptoms
Behaviors and functional deficiencies seen in schizophrenia vary widely among patients.
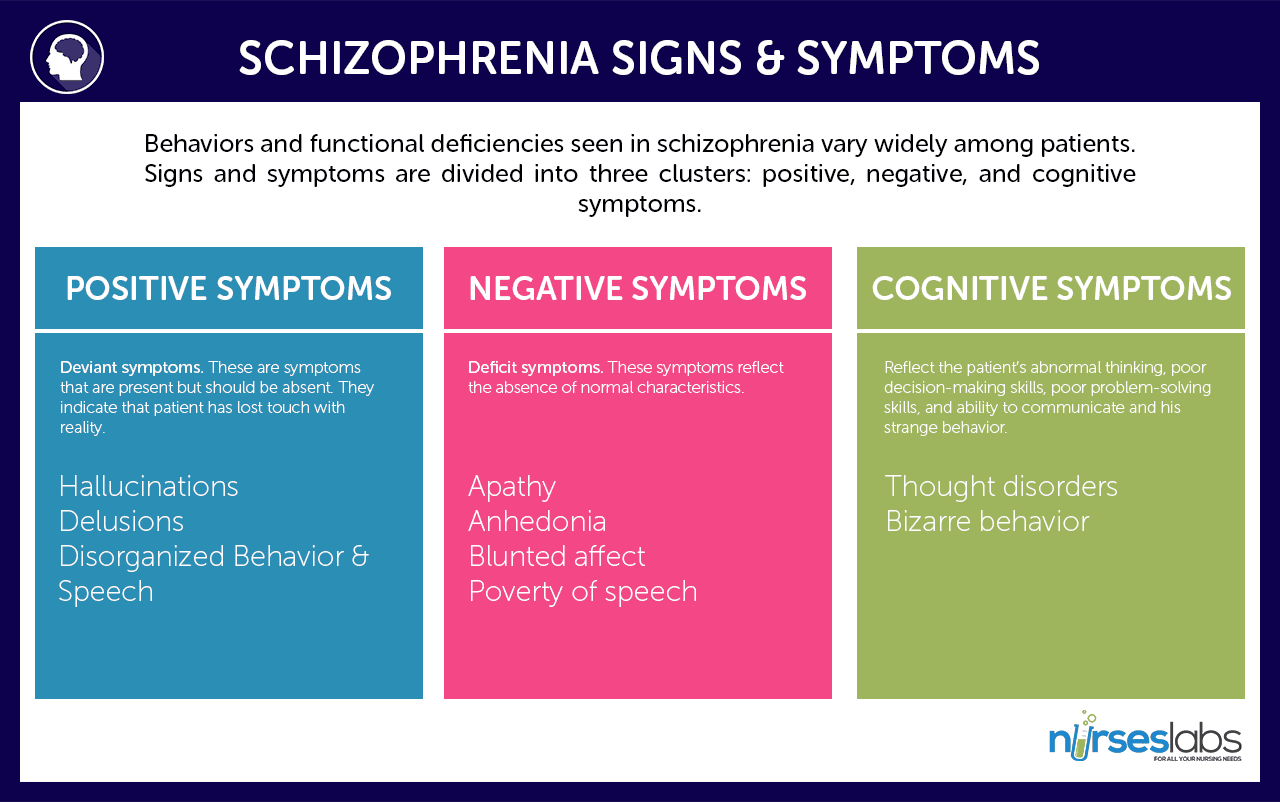
- Signs and symptoms are divided into three clusters: positive, negative, and cerebral symptoms.
- Positive symptoms are associated with temporal lobe abnormalities.
- Negative symptoms are associated with frontal cortex and ventricular abnormalities.
Positive Symptoms
- Deviant symptoms. These are symptoms that are present only should exist absent-minded . They indicate that patient has lost touch with reality.
- Primarily include delusions and hallucinations.
- Hallucinations are the nigh common feature of schizophrenia. These involve hearing, seeing, smelling, tasting, and feeling touched past things in the absence of stimuli. An example is hearing voices that command the patient to exercise certain things, usually abusive and self-destructive.
- Delusions are fixed fake beliefs. They cannot be changed by logic or persuasion. An example is a patient believing that people can read his mind. Several categories of delusions include:
- Persecutory delusions. Patient thinks he is beingness tormented, followed, tricked, or spied on.
- Reference delusions. Patient thinks that passages in books, music, TV shows, and other sources are directed at him.
- Delusions of thought withdrawal/thought insertion. Patient believes others can read his mind, his thoughts are beingness transmitted to others, or outside forces are imposing their thoughts or impulses on him.
Negative Symptoms
- Deficit symptoms. These symptoms reverberate the absence of normal characteristics.
- Apathy is lack of interest in people, things, and activities.
- Anhedonia is macerated chapters to feel pleasure.
- Blunted affect is characterized by patient'due south face appearing immobile and inexpressive; this is the flattening of emotions and becomes more pronounced as the illness progresses.
- Poverty of speech is a spoken communication that is brief and lacks content.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Reverberate the patient'southward abnormal thinking, poor controlling skills, poor problem-solving skills, and power to communicate and his strange behavior.
- Thought disorder is characterized by confused thinking and voice communication (due east.chiliad., incoherent ramblings, loose association, give-and-take salad, wandering).
- Bizarre beliefs include childlike silliness, laughing or giggling, agitation, inappropriate advent, hygiene, and comport.
Phases of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia ordinarily progresses through iii singled-out phases:
Prodromal Phase
- Occurs before hospitalization or inside the year.
- Characterized by clear pass up from his previous level of functioning.
- May withdraw from friends and families and hobbies and interests, exhibit peculiar behavior, and deterioration in work and school performance.
Agile Stage
- Commonly triggered by a stressful result
- Characterized by presence of acute psychotic symptoms (e.g. hallucinations, delusions, incoherence, and catatonic behaviors).
- Prognosis worsens with each acute episode.
Residual Phase
- This is at this signal in which illness pattern is established, inability level may be stabilized, and belatedly improvements may occur.
Types of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is classified into 5 subtypes:
Paranoid
- Characterized past persecutory or grandiose delusional thought content and delusional jealousy.
- Stress may worsen patient symptoms.
- Experience frequent auditory hallucinations but lack symptoms of other subtypes like incoherence, loose associations, and bear on issues.
- Tend to be less severely disabled than other schizophrenics and are more responsive to treatments.
Disorganized
- Marked by incoherent, disorganized speech communication and behaviors, and blunted or inappropriate impact.
- Usually includes extreme social harm.
- Starts early and insidiously, with no significant remissions.
"Knowing that you're crazy doesn't make the crazy things terminate happening."
–Marker Vonnegut, The Eden Express: A Memoir of Insanity
Catatonic
- A rare affliction form characterized by stock-still stupor or positions for long periods and periodically yielding to brief spurts of extreme excitement.
- Increased potential for destructive, violent behaviors when agitated.
- They remain mute and take refusal to move about or tend to personal needs.
Undifferentiated
- Presence of schizophrenic symptoms such equally delusions and hallucinations in patients who does not autumn to the category of the other subtypes.
Residual
- Muted form of the disease that stops brusk of recovery.
- No prominent psychotic symptoms.
- Has history of acute schizophrenic episodes and persistence of negative symptoms.
Diagnosis
The ground for diagnosing schizophrenia is formed by mental status exam, psychiatry history, and careful clinical ascertainment.
- Diagnostic test results. No definitive diagnostic tool for schizophrenia but sure tests like CT scan and MRI may be ordered to rule out disorders than tin cause psychosis (east.g. vitamin deficiencies and enlarged ventricles).
- Ventricular-brain ratio may detect elevated VBR in schizophrenic patients. Brain scans reveal functional cognitive asymmetries in a contrary pattern.
Medical Management
Here'southward how schizophrenia is medically managed:
- Drug Therapy. Schizophrenia is mainly treated by antipsychotics (neuroleptic) drugs.
- These forestall relapse of acute symptoms.
- Psychotic symptoms must be present 12 to 24 months before patients receive their first medical treatment.
- Examples of these drugs include the typical or conventional typical antipsychotic chlorpromazine (Thorazine) and the singular
- Electroconvulsive Therapy. Rarely used simply is for patients with acute schizophrenia and those who tin can't tolerate or don't respond to medication. It is constructive in reducing depressive and catatonic symptoms of schizophrenia.
- Other treatments include compliance promotion programs, psychosocial handling and rehabilitation, vocational counseling, supportive psychotherapy, and appropriate use of customs resources.
Nursing Management
Here are the nursing responsibilities for taking care of patients with schizophrenia:
Nursing Assessment
- Recognize schizophrenia. Note characteristic signs and symptoms of schizophrenia (eastward.g., speech abnormalities, thought distortions, poor social interactions).
- Establish trust and rapport. Don't tease or joke with patients. Expect that patient is going to put you lot through rigorous testing periods. Introduce yourself and explain your purpose.
- Maximize level of functioning. Assess patient's ability to carry out activities of daily living (ADLs).
- Assess positive symptoms.Assess for control hallucinations; explore answers. Assess if the client has fragmented, poorly organized, well-organized, systematized, or extensive arrangement of beliefs that are non supported by reality. Assess for pervasive suspiciousness virtually everyone and their actions (e.one thousand., vigilant, blames others for consequences of own behavior, belligerent, threatening).
- Assess negative symptoms.Assess for the negative symptoms of schizophrenia (as mentioned above).
- Assess medical history. Appraise if the client is on medications, what these are, and adherence to therapy.
- Assess support system.Determine whether the family is well informed about the affliction. Does the family sympathise the need for medication adherence?
Nursing Diagnoses
- Impaired Concrete Mobility related to depressive mood state and reluctance to initiate movement.
- Impaired Social Interaction related to problems in thought patterns and speech.
- Decreased Cardiac Output related to orthostatic hypotensive drug effects.
- Risk for Suicide related to impulsiveness and marked changes in behavior.
- Take chances for Injury related to hallucinations and delusions.
- Risk for Imbalanced Diet: less than torso requirements related to self-neglect and refusal for cocky-care.
Nursing Intendance Planning and Goals
Main Commodity: 6 Schizophrenia Nursing Care Plans
- Reduce severity of psychotic symptoms
- Prevent recurrence of astute episodes
- Come across patient'south' physical and psychosocial needs
- Help patient gain optimum level of performance
- Increase customer's compliance to handling and nursing programme
Nursing Interventions
- Establish trust and rapport. Don't impact customer without telling him start what y'all are going to practice. Utilise an accepting, consistent approach; curt, repeated contacts are best until trust has been established. Language should be articulate and unambiguous. Maintain a sense of promise for possible comeback, and convey this to the patient.
- Maximize level of functioning. Avoid promoting dependence by doing only what the patient tin can't practice for himself. Reward positive behavior and work with him to increment his personal sense of responsibility in improving functioning.
- Promote social skills. Provide support in assisting him to learn social skills.
- Ensure condom. Maintain a prophylactic environs with minimal stimulation.
- Ensure adequate nutrition.Monitor patient'southward nutritional status and if the patient thinks his food is poisoned, let him set his ain nutrient if possible or offer him foods in closed containers that he can open. Establish suicide and/or homicide precautions as appropriate.
- Go on it real. Engage patient in reality-oriented activities that involve human being contact (e.one thousand., workshops, inpatient social skills training). Clarify private language, autistic inventions, or neologisms.
- Bargain with hallucinations by presenting reality. Explore the content of hallucinations. Avert arguing about the hallucinations. Tell them you practice not see, hear, odor, or feel it but explain that you know that these hallucinations are real to him.
- Promote compliance and monitor drug therapy. Administer prescribed drugs and encourage the patient to comply. Ensure that patient is really taking the drug. Notice for manifestations that warrant hypersensitivity reactions and toxicity.
- Encourage family interest. Involve family in patient treatment and teach members to recognize impending relapse (e.chiliad. nervousness, indisposition, decreased power to concentrate). Advise ways how families tin manage symptoms.
Evaluation
- Evaluate effectiveness of drug therapy (absence of acute episodes and psychotic symptoms).
- Evaluate compliance to health instructions (taking medications on time, showing independence in activities, interest of family).
- Level of patient'southward functioning (ability to engage in social interactions).
- Patient'southward mental status (oriented to reality).
Documentation Guidelines
The following are to be documented in the patient's chart:
- Document the assessed presenting signs and symptoms (e.g., positive and negative signs).
- In instituting suicide precaution, document behavior and your precautions.
- In instituting homicide precaution, document patient's comment and who was notified. Exist sure to notify the doctor and the potential victim.
- In using restraints, document time of application and release.
Exercise Quiz: Schizophrenia
Here's a v item quiz nigh Schizophrenia. If you demand more visit our NCLEX page andNCLEX Psychiatric Nursing: Schizophrenic Disorders (xv Items)
1. The nurse would be correct in associating paranoid symptoms to increase in which neurotransmitter?
A. Prostaglandin
B. Dopamine
C. Norepinephrine
D. Serotonin
ii. A newly admitted patient tin't take care of his personal needs, shows insensitivity to painful stimuli, and exhibits negativism. The nurse would allocate the patient in which subtype?
A. Paranoid schizophrenia
B. Remainder schizophrenia
C. Catatonic schizophrenia
D. Undifferentiated schizophrenia
3. Which of the following are negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
A. aloofness and mirage
B. lack of motivation, blunted affect, and apathy
C. baroque behavior and delusions
D. asociality, anhedonia, and periodic excitability
4. The statement made by Steve "My co-workers envy me and are out to take me down. I swear they take hidden cameras everywhere I go!" would be documented equally:
A. Magical thinking
B. Hallucinations
C. Delusions
D. Normal finding, and would warrant police investigation.
five. The post-obit are atypical antipsychotics, except:
A. Olanzapine
B. Seroquel
C. Prolixin
D. Risperidone
Answers and Rationale
1. Answer: B. Dopamine.
Delusional or paranoid symptoms are associated with increased dopamine activity. Norepinephrine is associated with positive schizophrenic symptoms.
2. Answer: C. Catatonic schizophrenia.
- C: The following symptoms mentioned are unique to catatonic schizophrenia. It is also characterized by rigidity, negativism, and posturing.
- A: Paranoid schizophrenia is usually manifested by hallucinations and delusions.
- B: Residuum schizophrenia is characterized by history of at least one episode of acute schizophrenia.
- D: Undifferentiated schizophrenia is characterized by grossly disorganized behavior and prominent hallucinations.
3. B. lack of motivation, blunted affect, and apathy.
Negative symptoms are also called as deficit symptoms.
four. Respond: C. Delusions.
These are false ideas and are accepted past the patient as true. Specifically, this is mirage of persecution.
5. Reply: C. Prolixin
References
- Diagnostic and Statistical Transmission of Mental Disorders (DSM-5-TR)
- Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales
- Directly A's in Psychiatric & Mental Health Nursing: A Review Series
External Links & Further Reading
- Schizophrenia – National Institute of Mental Health – provides up to engagement information well-nigh Schizophrenia.
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Success: A Q&A Review Applying Critical Thinking to Exam Taking (Davis's Success) – great if you're reviewing for the NCLEX.
caldwellassitiony.blogspot.com
Source: https://nurseslabs.com/schizophrenia/
0 Response to "Studies of Family Concordance Patterns for Schizophrenia Have Found"
Post a Comment